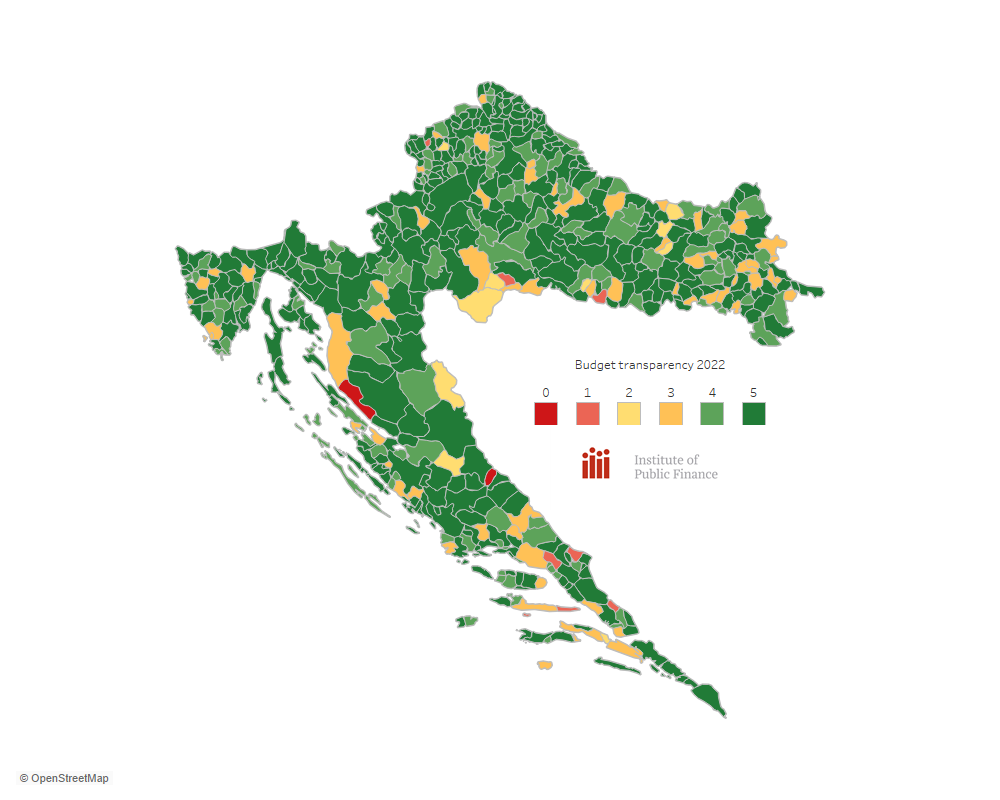
Transparent budgets are so framed as to provide citizens with complete, accurate, timely and understandable budget information. In turn, better-informed citizens can exert pressure on the collection of public funds and the supply of public goods and services, making them more efficient and increasing the accountability of regional/local authorities while reducing the opportunities for corruption. Maps show regional/local budget transparency measured by the number of the following key budget documents published on the official websites of the counties, cities and municipalities:
- 2020 year-end report
- 2021 mid-year report
- 2022 budget proposal
- 2022 enacted budget
- 2022 citizens budget
This analysis involved only the documents available in the period from November 2021 to April 2022, i.e. on the days when the websites were examined. Subsequently published documents were not considered. This methodology results in a regional/local budget transparency index ranging from zero to five.
Detailed results are presented in the IPF Notes Budget transparency in Croatian Counties, Cities and Municipalities: November 2021 - April 2022.
This work has been supported in part by the Croatian Science Foundation under the project (IP-2019-04-8360). Given the extensiveness of the research, there is some possibility of error. All the links were active at the time of the research.
Contact: transparency@ijf.hr.
How was the level of transparency of local budgets measured?
As it is not always easy to determine whether a budget document is published on the official websites of counties, cities and municipalities, the level of transparency was measured according to the following criteria:
- Enacted budget – if published on a regional/local government unit’s website or if there is a clearly stated direct link to a website containing that document. If published in a regional/local government unit’s official gazette, it is deemed to be published only if there is a clearly stated direct link to this particular document (e.g. ‘the 2022 budget’) to the official gazette in which it can be found on the regional/local government unit’s website. Otherwise, the document is not deemed to be published on the regional/local government unit’s website. Such a decision was taken in response to the frequently inadequate searchability of official gazettes.
- Budget proposal – if a document bearing this title is published on a regional/local government unit's website, if it is published on the same website as a 'draft budget proposal', if it is published as part of materials for a meeting, or if there is a clearly stated direct link to a website containing that document.
- Mid-year and year-end reports – if published on a regional/local government unit’s website under those titles, or as proposals for (drafts of) mid-year/year-end budget reports, as part of materials for a meeting, or if there is a clearly stated direct link to the websites containing such documents. If published in a regional/local government unit’s official gazette, they are deemed to be published only if there is a clearly stated direct link on the regional/local government unit’s website to these particular documents (e.g. ‘the 2021 mid-year report’), or the official gazette in which they can be found.
- Citizens budget – if any kind of simplified budget documents, intended for citizens, has been published on a regional/local government unit’s website (e.g. “budgets in a nutshell”, presentations, guides or brochures), or if there is a clearly stated direct link to the websites containing such documents.
When was the level of transparency of local budgets measured?
Publication of the 2020 year-end and 2021 mid-year reports was examined from 1 November to 31 December 2021, and publication of the budget proposal, enacted budget and citizens budget for 2022, from 1 February to 15 April 2022. Before that, on 24 September 2021, an e-mail message was sent to all regional/local government units, informing them of the time and manner of examining their respective websites.
This analysis involved only the documents available on the websites of regional/local units in the specified research periods, i.e. on the day of the search of their website.
Documents published subsequently are deemed not to have been published. The observed periods were already generous for regional/local government units, as the websites were assessed well after the dates when the budget documents were required to have been produced. Timeliness is an essential feature of budget transparency, because without timely information citizens cannot be informed at the right moment and meaningfully participate in budget processes. Of course, there is a possibility that the researchers did not find the searched, although published documents, but this only means that the citizens would have a hard time finding them too, or that at the time of the search the documents could not be opened.
Basis for requesting documents
According to Article 10 of the Act on the Right of Access to Information, public authorities are required to publish on their official websites, in an easily searchable manner and in a machine-readable formamong other things, annual plans, work reports, financial reports and other relevant documents relating to their respective scopes of activity, data on the sources of financing, the budget, financial plan or any other relevant document showing the public authorities' revenues and expenditures, as well as data and reports on the execution of the budget, financial plan or another relevant document.
Article 12 of the Budget Act says that regional/local government units must publish, in their official gazettes, their respective budgets and budget projections, decisions on interim financing, amendments to the budgets, as well as the general and specific part of their year-end and mid-year reports. This article states that the mid-year and year-end reports, as well as the annual financial reports, must be published on the regional/local government units’ official websites. According to Article 144 of the new Budget Act, which was enforced on 1 January 2022, the budget and amendments to the budget, the decision on temporary financing and the mid-year and year-end reports must be published on the websites of regional/local units, as well as citizens budget relating to budget, amendments to the budget and the mid-year and year-end reports. This legal change will be reflected in the next cycle of this research, in which the following documents will be considered legally obligatory for publication on the regional/local government units’ official websites: year-end and mid-year reports, enacted budget and citizens budget.
Moreover, the Ministry of Finance, on its official website recommends local government units to publish: their budget proposal (when submitted to the representative body by the executive body, i.e. by 15 November); the enacted budget (when passed by the representative body, i.e. by the end of the year); the draft year-end report (when submitted to the representative body by the executive body, i.e. by 1 June for the previous year); the draft mid-year report (when submitted to the representative body by the executive body, i.e. by 15 September for the previous year); and a citizens budget accompanying the budget proposal which could be printed and/or posted on the websites (by 15 November). It also recommends that all materials relating to the budget and its revisions should be published in MS Word and Excel format, and proposes a single format for citizens, guides to be produced along with the local government units' budgets.
By the Decree on Compiling and Submitting the Statement on Fiscal Responsibility and the Report on the Application of Fiscal Rules from October 2019, the Government sets additional requirements for local government units to improve budget transparency. Namely, in the Questionnaire on Fiscal Responsibility, local government units must answer whether they publish the enacted budget, the mid-year and year-end reports, and the citizens budget on their respective official websites.
Press corner
Here you can get all the materials related to the presentation of the local government units' budget transparency results: November 2020 – April 2021.
Archive of past researches
The Institute of Public Finance regularly analyses the budget transparency of counties, cities and municipalities.
The first and second research cycles (2013 and 2014) included all counties and cities and a sample of 100 municipalities (see Newsletters No. 81 and 87). Subsequent research cycles (2015, 2016, 2017, 2018, 2019, 2020 and 2021) included all 576 local government units (see Newsletters No. 97, 107, 112, 115, 117 and 119, and IPF Notes No. 119).
Thanks for the support
Presentation of this research is supported by: